Generational Differences in the Workplace
For the first time in history, there are five generations in the workplace. They are:
- Traditionalists—born 1925 to 1945
- Baby Boomers—born 1946 to 1964
- Generation X—born 1965 to 1980
- Millennials—born 1981 to 2000
- Generation Z—born 2001 to 2020
Check out the infographic below to learn how to manage different generations at work.
Complete this form to receive the Purdue Global program guide.
Challenges for Today's Employers
What kinds of challenges does this present for today’s employers? How do generational workforce differences affect our ability to manage people effectively? And what are the traits, beliefs, and life experiences that mark each generation, influencing how they work, communicate, and respond to change?
That’s precisely what this infographic is about. We spoke with Bea Bourne, DM, faculty member in the School of Business and Information Technology at Purdue Global. Dr. Bourne is an expert on generational differences and generational response to organizational change. In this infographic, she shares her research regarding:
- How today’s talent stacks up by generation, including their defining values, beliefs, and worldviews
- The significant historical events that shaped each generation
- How to best motivate and manage workers from each generation
With this information, managers and HR executives can develop multigenerational strategies in recruitment, orientation, talent management, retention, and succession planning.
Generational Differences in the Workplace Infographic Content
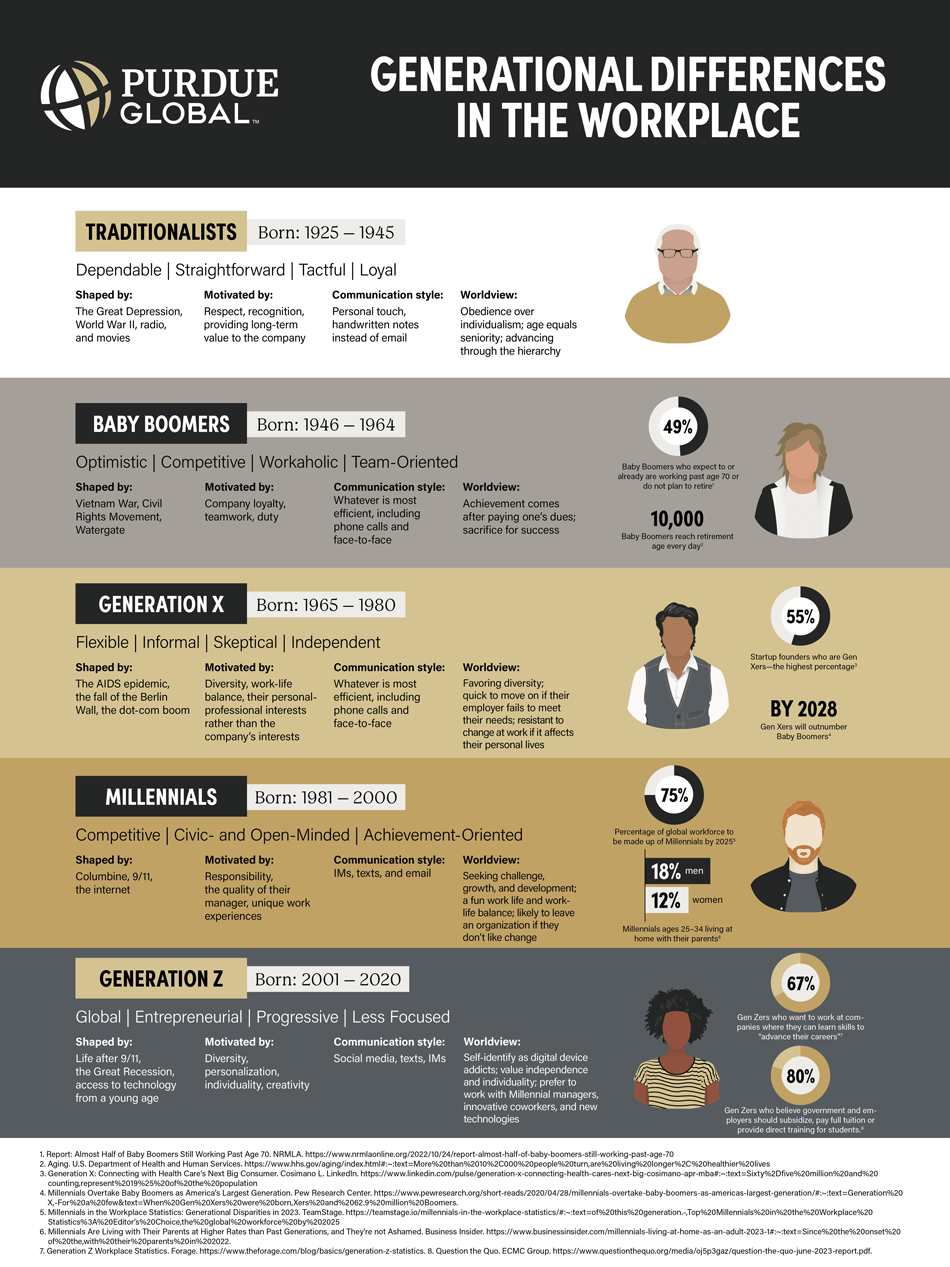
Traditionalists
Born: 1925–1945
Dependable, straightforward, tactful, loyal
Shaped by: The Great Depression, World War II, radio, and movies
Motivated by: Respect, recognition, providing long-term value to the company
Communication style: Personal touch, handwritten notes instead of email
Worldview: Obedience over individualism; age equals seniority; advancing through the hierarchy
Baby Boomers
Born: 1946–1964
Optimistic, competitive, workaholic, team-oriented
Shaped by: The Vietnam War, civil rights movement, Watergate
Motivated by: Company loyalty, teamwork, duty
Communication style: Whatever is most efficient, including phone calls and face-to-face
Worldview: Achievement comes after paying one’s dues; sacrifice for success
Stats:
- 49% of Baby Boomers expect to or already are working past age 70 or do not plan to retire1
- 10,000 Baby Boomers reach retirement age every day2
Generation X
Born: 1965–1980
Flexible, informal, skeptical, independent
Shaped by: The AIDs epidemic, the fall of the Berlin Wall, the dot-com boom
Motivated by: Diversity, work-life balance, their personal-professional interests rather than the company's interests
Communication style: Whatever is most efficient, including phone calls and face-to-face
Worldview: Favoring diversity; quick to move on if their employer fails to meet their needs; resistant to change at work if it affects their personal lives
Stats:
- 55% of startup founders are Gen Xers — the highest percentage3
- By 2028, Gen Xers will outnumber Baby Boomers4
Millennials
Born: 1981–2000
Competitive, civic- and open-minded, achievement-oriented
Shaped by: Columbine, 9/11, the internet
Motivated by: Responsibility, the quality of their manager, unique work experiences
Communication style: IMs, texts, and email
Worldview: Seeking challenge, growth, and development; a fun work life and work-life balance; likely to leave an organization if they don't like change
Stats:
- 75% percent of the global workforce will be made up of Millennials by 20255
- 18% of Millennial men ages 25–34 live at home with their parents6
- 12% of Millennial women ages 25–34 live at home with their parents6
Generation Z
Born: 2001–2020
Global, entrepreneurial, progressive, less focused
Shaped by: Life after 9/11, the Great Recession, access to technology from a young age
Motivated by: Diversity, personalization, individuality, creativity
Communication style: Social media, texts, IMs
Worldview: Self-identifying as digital device addicts; valuing independence and individuality; prefer to work with Millennial managers, innovative coworkers, and new technologies
Stats:
- 67% of Gen Zers want to work at companies where they can learn skills to advance their careers7
- 80% of Gen Zers believe government and employers should subsidize, pay full tuition, or provide direct training for students8
References:
- Report: Almost Half of Baby Boomers Still Working Past Age 70. NRMLA.
- Aging. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
- Generation X: Connecting with Health Care’s Next Big Consumer. Cosimano L. LinkedIn.
- Millennials Overtake Baby Boomers as America’s Largest Generation. Pew Research Center.
- Millennials in the Workplace Statistics: Generational Disparities in 2023. TeamStage.
- Millennials Are Living with Their Parents at Higher Rates than Past Generations, and They’re not Ashamed. Business Insider.
- Generation Z Workplace Statistics. Forage.
- Question the Quo. ECMC Group.